chest compression sternum fracture test|sternum fracture prognosis : wholesale Traumatic sternal fractures are found in up to 8% of blunt chest trauma patients and 18% of polytrauma patients with thoracic injuries, amid only sporadic cases secondary to penetrating . Jogos em destaque.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webComedian Capi Pérez travels back to Aguascalientes, his hometown, making a spectacular entrance. His comedy jokes about the local culture, like avoidi.
sternum fracture symptoms
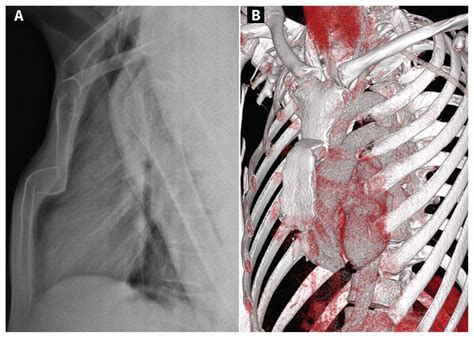
A lateral chest radiograph remains the gold standard investigation in diagnosing sternal fractures, as the fracture and any displacement or dislocation occurs in the sagittal plane.
The sternum – sometimes called the breastbone – is the flat bone in the center of your chest. Your ribs and collarbone connect to your sternum. A break in your sternum is also .
With the patient lying on his side, examiner should stand beside the patient with both hands on the patient’s lateral trunk (side of the rib cage) that is up. With patient standing, sitting, or lying . Chest computed tomography — Chest CT is highly accurate for showing the location and number of rib fractures but should not be performed for the sole purpose of .
Traumatic sternal fractures are found in up to 8% of blunt chest trauma patients and 18% of polytrauma patients with thoracic injuries, amid only sporadic cases secondary to penetrating . Sternal fracture–associated mortality can result from cardiac contusion, aortic rupture, pulmonary contusion, and thoracic spine compression fractures. Sternal and rib fractures are common.Sternal fractures can only be detected in a frontal chest plain film when it is associated with significant tansverse displacement. A CT scan identifies almost all sternal fractures, displacements, internal thoracic injuries and retrosternal . A lateral chest radiograph remains the gold standard investigation in diagnosing sternal fractures, as the fracture and any displacement or dislocation occurs in the sagittal plane.
sternum fracture surgery
Sternum. Key points. Look for a step in the cortex of the sternum. Don't mistake the sternomanubrial junction for a fracture. Fractures of the sternum are often due to direct trauma such as a road traffic crash, but may also be caused by chest . CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) chest compressions on an injured patient may also result in a fracture of the sternum. It is possible that fractures of the breastbone also happen with considerably less force. For .Sternal fractures are frequently diagnosed using a lateral chest x-ray or CT scan of the chest. Sternal fractures increase the risk of and are commonly associated with other injuries. The disposition of patients with a sternal fracture is .
INTRODUCTION — . Multiple vital thoracic structures are at risk of injury from blunt chest trauma such as rapid deceleration and direct injury. Major concerns include chest wall injury (eg, rib fractures or flail chest), cardiovascular injury (eg, blunt aortic injury [BAI] or cardiac contusion), and pulmonary injury (eg, pneumothorax, contusions, or lacerations). Hitting your chest on the steering wheel or slamming against a seatbelt can both bruise your sternum. . You may also need a chest X-ray to make sure you don’t have a sternal fracture. Bruises . Examination — Signs of rib fractures include point tenderness on a specific rib or focal tenderness caused by compression of the ribcage distant from the site of pain. Bony crepitus and ecchymosis may be present. . — In patients with suspected rib fractures or chest wall trauma, chest radiographs (CXRs) are obtained primarily to rule out .
Purpose of Test: To identify the effect of vertebral compression to the patient’s symptoms. Test Position: Sitting. Performing the Test: Apply an inferiorly directed pressure through the superior aspects of both shoulders. A positive response is an indication of pain. Diagnostic Accuracy: Unknown. Importance of Test: With a reproduction of pain, it could signal tissue trauma, .
Sternal fractures are often seen in association with deceleration injuries and/or direct blows to the chest, as in blunt chest trauma during motor vehicle accidents. [] The introduction of seat-belt legislation has resulted in an increased frequency of these types of injuries. [2, 3, 4] Fractures are also a common complication of the repeated sternal .Managing chest wall injuries What is a chest wall injury? Injuries to the chest wall include fractured ribs, fractured sternum (breastbone) and/or bruising to the lungs. They normally occur following an impact trauma to the chest, such as falling from a height, a road traffic accident or during impact sports. Signs and symptoms In the past few decades, the compression point described in different guidelines did not change significantly. 11, 14 And the lower part of sternum is recommended for hand placement by the AHA guideline, 11 based on the results of two small studies. 15, 16 In the study by Cha et al., 15 the authors found SPO2 and peak arterial pressure were .
Flail chest is a traumatic injury that makes it difficult to breathe. Car accidents are the major cause. . The fractures cause your ribs and chest wall to malfunction in the ways they move. This movement, called paradoxical, means the injured section of your chest wall moves in an opposite direction when compared with your undamaged chest wall. We examined chest injuries related to chest compressions, classified as follows: rib fracture, sternal fracture, and other uncommon complications. We enrolled 185 patients in this study. The most frequent complication to occur in both groups was rib fracture: 27 (62.8%) and 112 (78.9%) patients in the pre-2010 and post-2010 groups, respectively .
Chest pain after cardiac arrest is typically caused by injuries sustained during CPR. Forceful and repeated chest compressions, combined with electric shocks from defibrillation, can bruise or even break ribs and damage chest cartilage or the breastbone (sternum). Lung injuries like a collapsed lung are also possible, though less common. Rib fractures occur when a significant enough force directed at the rib causes a break. There are a total of 12 pairs of ribs in the thoracic region. The first seven ribs attach anteriorly to the sternum and posteriorly to the spinal column. Rib numbers 8 through 10 attach similarly but connect to the costal cartilage of the sternum anteriorly. Ribs 11 and 12 have the .
Cardiac and respiratory causes will need to be ruled out. If the patient complains of radiating pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, exertional chest pain, fever, or productive cough these are symptoms that may indicate different and more serious causes of chest pain. If there has been trauma an occult rib fracture should also be considered.
sternum fracture prognosis
Introduction. American Heart Association (AHA) and European Resuscitation Council (ERC) Guidelines 2015 for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) specify that chest compressions should be delivered with a depth of at least 5 cm but not greater than 6 cm at a rate of 100–120/min. 1, 2 These specifications are rarely met: compression depth with manual .Traumatic sternal fractures are rare, with two distinct clinicopathologic entities with different prognosis and management. Isolated sternal fractures are commonly benign injuries that can be managed conservatively in an outpatient setting. Polytrauma patients with sternal fractures should be carefully screened for associated injuries. Compressions at the left ventricle increase rate of return of spontaneous circulation. This study aimed to identify the landmark of the point of maximal left ventricular diameter on the sternum (LVmax) by using chest computed tomography (CCT) in the arms-down position, which was similar to an actual cardiac arrest patient. Chest compressions are a cornerstone of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Recent work confirms the importance of early compressions to improve survival [].Oxygen is present in the blood up to ten minutes after arrest; re-establishing circulation of this blood via sternal compressions is the most important step of the ABCs early in resuscitation []. .
Unfortunately, several studies found that mechanical chest compression does not seem to improve outcomes after OHCA when compared with manual chest compression [14–16]. In addition, chest compression cannot be effectively applied under some circumstances, such as in patients with chest wall deformities, rib fractures, or haemopneumothorax. The objective of this study was to determine the height of optimal hand position for chest compression during adult cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) from the tip of the sternal xiphoid process . Thoracic Orthopaedic Tests Palpation Anterior Aspect Sternum Descriptive Anatomy The sternum, which lies at the anterior part of the chest wall, consists of three parts: the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. It articulates with the costal cartilages on both sides. The manubrium also articulates with the facets of the clavicle on both sides (Fig. 9-1).. High quality chest compressions are the cornerstone of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), but it is a complex task to find a balance between the benefit of increased compression depth, cardiac output, and the risk of harming the patient. . (0–6)] (p = 0.021). The proportion of patients with sternum fractures was higher in the groups .
Education video describing the types of sternal fractures. Fractures of the sternum are fractures to the bone located in the center of the chest. These injur.
A sternal fracture is a fracture of the sternum (the breastbone), located in the center of the chest.The injury, which occurs in 5–8% of people who experience significant blunt chest trauma, may occur in vehicle accidents, when the still-moving chest strikes a steering wheel or dashboard [1] or is injured by a seatbelt. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), has also been known to . Fracture of sternum associated with chest compression and cardiopulmonary resuscitation. 2023 - New Code 2024 2025 Billable/Specific Code. M96.A1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.; Short description: Fx sternum assoc with chest comprsn and cardiopulm resusSternal fractures are breaks in the sternum, often caused by trauma, and can be associated with other injuries. Introduction. Survival after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) depends on multiple factors. One of the most important is the quality and timing of basic life support, consisting mainly of chest compressions and early defibrillation 1–4.To ease the difficulty of effective manual compression in the prehospital/patient transport setting, 5 researchers developed the .
sternum fracture healing
Portable Digital Nut Moisture Meter Brand manufacturer
web18 de mar. de 2023 · Freegans will eat any food product as long as it’s free. Some freegans do this because they don’t want to give money to food producers who harm animals, the .
chest compression sternum fracture test|sternum fracture prognosis